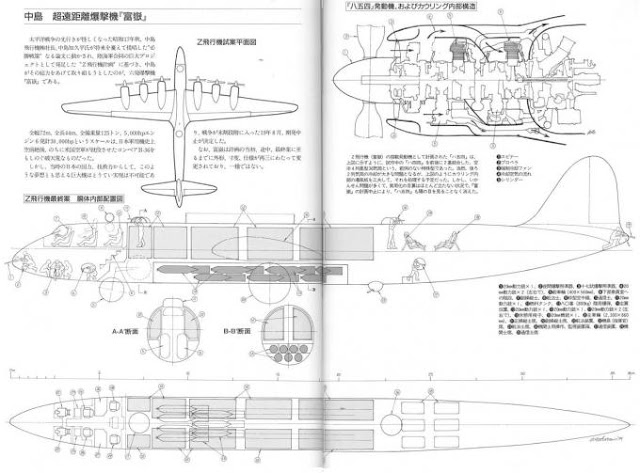
Era un bombardiere giapponese a lungo raggio progettato alla fine della seconda guerra mondiale. Fu concepito per attacchi aerei strategici a lungo raggio dal Giappone contro obiettivi industriali lungo la costa occidentale (ad es. San Francisco) e nel Midwest (ad es. Detroit, Chicago e Wichita) e nel nord - est (ad es. New York City e Norfolk ) degli Stati Uniti. Il peggioramento della situazione bellica del Giappone portò alla cancellazione del progetto nel 1944 e nessun prototipo fu mai costruito.
Progettazione e sviluppo
Il Fugaku ebbe origine nel "Progetto Z (progetto del bombardiere)", una specifica dell'esercito giapponese imperiale del 1942 per un bombardiere intercontinentale che poteva decollare dalle Isole Curili, bombardare gli Stati Uniti continentali, e poi fare scalo nella Francia occupata dai tedeschi. Una volta lì, sarebbe stato rifornito di carburante e riarmato per un'altra sortita di ritorno.
Il progetto Z prevedeva tre varianti:
- Un bombardiere pesante,
- Un trasporto (capace di trasportare 300 truppe),
- Uno armato con un cannone e quaranta mitragliatrici che sparavano verso il basso dalla fusoliera per attacchi di terra intensi al ritmo di 640 colpi al secondo (38.400 colpi al minuto).
Il progetto fu progettato dal capo della società Nakajima, Chikuhei Nakajima. Il design aveva ali diritte ed eliche a quattro pale contro-rotanti. Per risparmiare peso, alcuni dei carrelli di atterraggio dovevano essere sganciati dopo il decollo (non essendo necessari all'atterraggio senza carico di bombe), proprio come alcuni progetti tedeschi dello stesso periodo. Utilizzava sei motori, come con i parlasse tedeschi Amerika Bomber, per sopperire alla scarsa potenza (2.000 CV) di ciascuno.
Lo sviluppo fu iniziato nel gennaio del 1943 e fu costruito un impianto di progettazione e produzione a Mitaka, Tokyo. Il motore Ha-54 (Ha-505) a 4 cilindri da 36 cilindri Nakajima fu abbandonato perché troppo complesso.
Il progetto Z fu annullato nel luglio del 1944 e il Fugaku non fu mai costruito.
Operatori (pianificato)
Giappone - Imperial Air Navy Navy Service - (G10N / Fugaku) - Imperial Japanese Army Air Force - (Progetto Z).
Specifiche (progetto Z / progetto Fugaku)
Caratteristiche generali:
- Equipaggio: da 6 a 10;
- Fugaku: dalle 7 alle 8 - Lunghezza: 44,98 m (147 ft 7 in)
- Fugaku: 39,98 m (131 piedi) - Apertura alare: 64,98 m (213 ft 2 in)
- Fugaku: 62,97 m (207 piedi) - Altezza: 8,77 m (28 ft 9 in) - Superficie alare: 352,01 m 2 (3.789,0 piedi quadrati)
- Fugaku: 330 m 2 (3.552,09 piedi quadrati) - Proporzioni: 12.1 - Peso a vuoto: 65.000 kg (143.300 lb)
- Fugaku: 33.800 kg (74.516,24 libbre) - Peso lordo: 122.000 kg (268.964 lb)
- Fugaku: 42.000 kg (92.594,15 libbre) - Peso massimo al decollo: 160.000 kg (352.740 lb)
- Fugaku: 70.000 kg (154.323,58 libbre) - Motopropulsore: 6 × Nakajima Ha-54 36 cil. motori a pistoni radiali raffreddati ad aria, 3.700 kW (5.000 CV) ciascuno al decollo
- Fugaku: 6x Nakajima NK11A 18 cilindri. motori a pistoni radiali raffreddati ad aria che sviluppano 2.500 CV (1.864 kW) al decollo
- Eliche: eliche controrotanti a velocità costante a 6 pale, diametro 4,5 m (14 ft 9 in)
- Fugaku: eliche a 4 pale a velocità costante con diametro di 4,8 m (16 piedi).
Prestazioni:
- Velocità massima: 679 km / h (422 mph, 367 kn) a 10.000 m (32.808 ft)
- Fugaku: 779 km / h (484 mph) a 10.000 m (32.808 piedi) - Autonomia: massimo 17.999 km (11.184 mi, 9.719 nmi)
- Fugaku: 19.400 km (12.055 mi) - Max di servizio: 15.000 m (49.000 ft) - Carico alare: 456,99 kg / m 2 (93,60 lb / sq ft)
- Fugaku: 211,89 m 2 (43,4 lb / ft 2 ) - Potenza / massa : 0,103 kW / kg (0,063 CV / lb)
- Fugaku: 0,118 kW / kg (0,07 CV / lb).
Armamento:
- Cannoni: 4 × 20mm Tipo 99
- Bombe: 20.000 kg (44.092 libbre) di bombe.
ENGLISH
The Nakajima G10N Fugaku (Japanese: 富岳 or 富嶽, "Mount Fuji"), was a planned Japanese ultra-long-range heavy bomber designed during World War II. It was conceived as a method for mounting aerial attacks from Japan against industrial targets along the west coast (e.g., San Francisco) and in the Midwest (e.g., Detroit, Chicago, and Wichita) and the northeast (e.g., New York City and Norfolk) of the United States. Japan's worsening war situation resulted in the project's cancellation in 1944 and no prototype was ever built.
Design and development
The Fugaku had its origins in "Project Z (bomber project)", a 1942 Imperial Japanese Army specification for an intercontinental bomber which could take off from the Kuril Islands, bomb the continental United States, then continue onward to land in German-occupied France. Once there, it would be refueled and rearmed and make another return sortie.
Project Z called for three variations on the airframe: heavy bomber, transport (capable of carrying 300 troops), and a gunship armed with forty downward-firing machine guns in the fuselage for intense ground attacks at the rate of 640 rounds per second (i.e. 38,400 rounds per minute).
The project was conceived by Nakajima Aircraft Company head Chikuhei Nakajima. The design had straight wings and contra-rotating four-blade propellers. To save weight, some of the landing gear was to be jettisoned after takeoff (being unnecessary on landing with emptied bomb load), as had been planned on some of the more developed German Amerika Bomber competing designs. It used six engines, as with the later Amerika Bomber design competitors, to compensate for nearly all German aircraft engines being limited to 1,500 kW (2,000 hp) maximum output levels apiece.
Development was initiated in January 1943 and a design and manufacturing facility built in Mitaka, Tokyo. Nakajima's 4-row 36-cylinder 5,000 hp Ha-54 (Ha-505) engine was abandoned as too complex.
Project Z was cancelled in July 1944, and the Fugaku was never built.
Operators (planned)
Japan - Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service – (G10N / Fugaku) - Imperial Japanese Army Air Force – (Project Z).
Specifications (Project Z / Fugaku projected)
General characteristics:
Crew: 6 to 10;
- Fugaku: 7 to 8 - Length: 44.98 m (147 ft 7 in)
- Fugaku: 39.98 m (131 ft) - Wingspan: 64.98 m (213 ft 2 in)
- Fugaku: 62.97 m (207 ft) - Height: 8.77 m (28 ft 9 in) - Wing area: 352.01 m2 (3,789.0 sq ft)
- Fugaku: 330 m2 (3,552.09 sq ft) - Aspect ratio: 12.1 - Empty weight: 65,000 kg (143,300 lb)
- Fugaku: 33,800 kg (74,516.24 lb) - Gross weight: 122,000 kg (268,964 lb)
- Fugaku: 42,000 kg (92,594.15 lb) - Max takeoff weight: 160,000 kg (352,740 lb)
- Fugaku: 70,000 kg (154,323.58 lb) - Powerplant: 6 × Nakajima Ha-54 36-cyl. air-cooled radial piston engines, 3,700 kW (5,000 hp) each at take-off
- Fugaku: 6x Nakajima NK11A 18-cyl. air-cooled radial piston engines developing 2,500 hp (1,864 kW) at take-off
- Propellers: 6-bladed contra-rotating constant speed propellers, 4.5 m (14 ft 9 in) diameter
- Fugaku: 4-bladed constant speed propellers 4.8 m (16 ft) diameter.
Performance:
- Maximum speed: 679 km/h (422 mph, 367 kn) at 10,000 m (32,808 ft)
- Fugaku: 779 km/h (484 mph) at 10,000 m (32,808 ft) - Range: 17,999 km (11,184 mi, 9,719 nmi) maximum
- Fugaku: 19,400 km (12,055 mi) - Service ceiling: 15,000 m (49,000 ft) - Wing loading: 456.99 kg/m2 (93.60 lb/sq ft)
- Fugaku: 211.89 m2 (43.4 lb/ft2) Power/mass: 0.103 kW/kg (0.063 hp/lb)
- Fugaku: 0.118 kW/kg (0.07 hp/lb).
Armament:
- Guns: 4× 20mm Type 99 cannon
- Bombs: 20,000 kg (44,092 lb) of bombs.
(Web, Google, Wikipedia, You Tube)