Le due squadre in competizione per il futuro requisito della Luftwaffe Schwerer Transporthubschrauber (elicottero da trasporto pesante, STH) hanno ancora intenzione di offrire i loro elicotteri dopo che la Bundeswehr ha annullato la gara. Il 29 settembre 2020 il ministero della Difesa tedesco ha confermato ai media che la gara era stata annullata perché "sarebbe improbabile che venga realizzata entro il budget assegnato pur rispettando tutti i requisiti".
Il parlamento tedesco, ha stanziato 5,6 miliardi di €uro per il programma STH nel novembre 2018, ma i due concorrenti (il Boeing CH-47F e il Sikorsky CH-53K) sarebbero costati circa 10 miliardi di Euro. La Rheinmetall, che è il partner principale del team Sikorsky, concorre con il CH-53K.
Nel suo comunicato stampa, il Ministero della Difesa tedesco ha affermato che il requisito STH sarebbe stato riesaminato ma che un contratto non sarebbe stato pronto nel 2021, sebbene l'obiettivo sia ancora quello di sostituire il CH-53G, la cui durata di servizio termina nel 2030. Il ministero ha ribadito che il progetto STH è di altissima priorità per la Bundeswehr, poiché il trasporto aereo è di fondamentale importanza per la mobilità e la reattività delle forze armate, nonché per i servizi umanitari e di supporto. Il progetto sarà quindi proseguito con specifiche modificate.
Il Sikorsky CH-53K King Stallion è la nuova versione, in fase di sviluppo, del più grande e pesante elicottero in dotazione allo United States Marine Corps Aviation, il Sikorsky CH-53E Sea Stallion.
Sviluppo
Il Corpo dei Marines aveva programmato di aggiornare la maggior parte dei suoi CH-53E per tenerli più a lungo in servizio, ma questo progetto entrò in una fase di stallo. La Sikorsky, avendo appurato l'interesse dei Marines per un aggiornamento della macchina, propose una nuova versione in origine denominata "CH-53X". Accettata questa nuova variante, nell'aprile 2006, l'USMC firmò un contratto del valore di 18,8 miliardi di dollari per 156 esemplari costruiti ex novo che furono denominati "CH-53K", da consegnarsi entro il 2021. I marines avevano in programma di iniziare a ritirare i CH-53E nel 2009 ed avevano bisogno dei nuovi elicotteri molto rapidamente perché alcune cellule avrebbero iniziato ad accusare limiti strutturali di vita entro il 2011-12. Le prime prove in volo del CH-53K sarebbero dovute iniziare nel 2011. Il primo esemplare di serie è stato consegnato il 16 maggio 2018 per entrare nel Supportability Test Plan (STP) sulla Marine Corps Air Station (MCAS) a Jacksonville, nella Carolina del Nord. L'STP comporta una valutazione logistica sulla manutenzione, il mantenimento e il supporto complessivo del CH-53K, contestualmente alla convalida delle procedure di manutenzione con i manutentori dell'USMC. Garantirà prontezza e supporto sulla linea di volo fino a quando il CH-53K entrerà in servizio verso la fine del 2019.
Progettazione
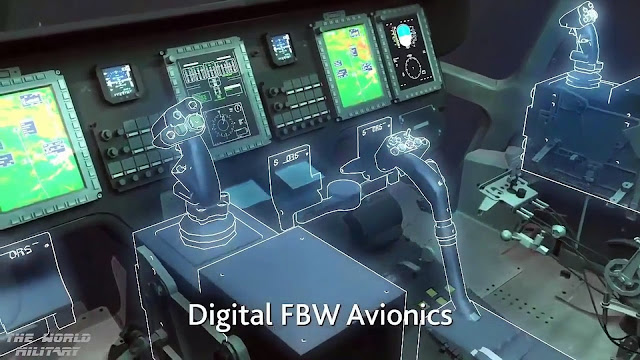
Il CH-53K è una riprogettazione generale del CH-53E Sea Stallion. I principali miglioramenti sono nuovi motori e una cabina di pilotaggio riprogettata, dotata di strumentazione completamente digitale e comandi fly-by-wire. Il CH-53K avrà più del doppio della capacità di sollevamento e del raggio di azione del CH-53E e una stiva più ampia per permettere di trasportarvi un Humvee. Sarà caratterizzato da nuovi sponson in materiale composito di forma più tozza e stretta, in modo da ridurre la larghezza complessiva, dando così all'elicottero un'impronta a terra più contenuta nelle operazioni a bordo delle portaerei d'assalto anfibio.
Avrà, inoltre, un rotore dotato di nuove pale in materiali compositi, con tecnologia simile a quella attualmente presente sull'UH-60 Black Hawk. Le tre turbine utilizzate saranno le General Electric GE38-1B. Questa turbina è stata scelta in una rosa di concorrenti che comprendeva la turbina Pratt e Whitney Canada PW150 e una derivata dalla Rolls-Royce AE 1107C-Liberty utilizzata sul convertiplano V-22 Osprey.
Nel mese di agosto 2007, l'USMC ha aumentato il suo ordine di CH-53K da 156 a 227 esemplari. Quando entrerà in servizio, sarà utilizzato come elicottero da trasporto e sollevamento pesante, mentre l'Osprey sarà destinato a trasporti meno voluminosi e l'UH-1Y come elicottero utility.
Il 4 dicembre 2012 la Sikorsky ha consegnato il primo CH-53K, un banco di prova a terra per testare tutte le modifiche apportate, volte a migliorare le prestazioni della cellula. Il primo volo è avvenuto il 27 ottobre 2015. Interesse per questa nuova versione è stato mostrato da parte dell'aviazione israeliana che, nel 2009, ha dichiarato di voler valutare la nuova variante dopo il primo volo. Nel mese di agosto 2015, l'aviazione israeliana ha formalizzato un requisito per il CH-53K, precisando di voler sostituire i suoi CH-53 "Yasur" dopo il 2025, quando questi avranno esaurito le ore di volo disponibili.
Il CH-53K si distingue principalmente per la fusoliera più larga rispetto alle precedenti varianti della gamma CH-53, proprio per agevolare le procedure di carico ed aumentare il carico pagante. Per queste esigenze la potenza disponibile è stata accresciuta mediante l'adozione di tre turbine General Electric GE-38-1B in grado di generare fino a 7 500 shp ciascuna. L'elicottero raggiunge, quindi, 38 400 kg di peso massimo al decollo e può caricare fino a 16 tonnellate di carico o 37 soldati equipaggiati (fino a 55 con un'ulteriore fila centrale di posti). Il CH-53K ha una velocità di crociera di 315 km/h, un raggio d'azione di 200 km ed un'autonomia di oltre 850 km.
Potenziali utilizzatori:
- Germania - Nel febbraio 2018, Sikorsky sigla un accordo del valore di ca. 4 miliardi di Euro con Rheinmetall per il programma di sostituzione dei CH-53G della Bundeswehr, dove il CH-53K è in competizione con il Boeing CH-47 Chinook – Richiesta ufficiale di offerta per 41 esemplari emessa a fine 2018.
- Israele - Le Forze di difesa israeliane hanno mostrato interesse per il CH-53K nel 2009. Nell'agosto 2015, il Governo israeliano ufficializza l'interesse come "very high priority". L'attuale CH-53 "Yasur" rimarrà operativo fino al 2025. Israele – Forze di difesa israeliane –Richiesta di offerta per 20 esemplari.
- Giappone - Dimostrazione di interesse per il CH-53K.
Utilizzatori:
- Stati Uniti - United States Marine Corps Aviation - 24 CH-53K ordinati con un fabbisogno di 200 esemplari.
ENGLISH
Replacement of the German CH-53G by the "K" version
The two teams competing for the future requirement of the Luftwaffe Schwerer Transporthubschrauber (heavy transport helicopter, STH) are still planning to offer their helicopters after the Bundeswehr cancelled the tender. On 29 September the German Ministry of Defence (MoD) announced in a press release that the tender had been cancelled because 'it would be unlikely to be realised within the allocated budget while meeting all requirements'.
The Bundestag, the German parliament, committed EUR5.6 billion (USD6.6 billion) to the STH programme in November 2018, that the two competing proposals - the Boeing CH-47F and Sikorsky CH-53K - would have cost around EUR10 billion. Neither company has officially confirmed this to Janes, with Rheinmetall, which is the lead partner of the Sikorsky team offering the CH-53K, on 2 October citing the Public Procurement Act and Boeing stating on 1 October that it "cannot comment on commercial matters in live and ongoing negotiations with the BAAINBw".
In its press release, the German Ministry of Defence said that the STH requirement would be reviewed but that a contract would not be ready in 2021, although the aim is still to replace the CH-53G, whose service life ends in 2030, "in a timely manner". The ministry added: "the STH project is of the highest priority for the Bundeswehr, as air transport is of fundamental importance for the mobility and responsiveness of the armed forces, as well as for humanitarian and support services. The project will therefore be continued with specific modifications".
The Sikorsky CH-53K King Stallion is a heavy-lift cargo helicopter currently being produced by Sikorsky Aircraft for the United States Marine Corps (USMC). The design features three 7,500 shp (5,590 kW) engines, new composite rotor blades, and a wider aircraft cabin than previous CH-53 variants. It will be the largest and heaviest helicopter in the U.S. military. The USMC plans to receive 200 helicopters at a total cost of $25 billion. Ground Test Vehicle (GTV) testing started in April 2014; flight testing began with the maiden flight on 27 October 2015. In May 2018, the first CH-53K was delivered to the Marine Corps.
Development
H-53 background
The CH-53 was the product of the US Marine Corps' "Heavy Helicopter Experimental" (HH(X)) competition begun in 1962. Sikorsky's S-65 was selected over Boeing Vertol's modified CH-47 Chinook version. The prototype YCH-53A first flew on 14 October 1964. The helicopter was designated "CH-53A Sea Stallion" and delivery of production helicopters began in 1966. The CH-53A was equipped with two T64-GE-6 turboshaft engines, and had a maximum gross weight of 46,000 lb (20,865 kg).
Variants of the original CH-53A Sea Stallion include the RH-53A/D, HH-53B/C, CH-53D, CH-53G, and MH-53H/J/M. The RH-53A and RH-53D were used by the United States Navy for minesweeping. The CH-53D included a more powerful version of the General Electric T64 engine, used in all H-53 variants, and external fuel tanks. The US Air Force's HH-53B/C "Super Jolly Green Giant" were for special operations and combat rescue. The Air Force's MH-53H/J/M Pave Low helicopters were the last of the twin-engined H-53s, and were equipped with extensive avionics upgrades for all-weather operation.
In October 1967, the U.S. Marine Corps issued a requirement for a helicopter with a lifting capacity 1.8 times that of the CH-53D, that could fit on amphibious assault ships. Before this, Sikorsky had been working on an enhancement to the CH-53D, under the company designation "S-80", featuring a third turboshaft engine and a more powerful rotor system. Sikorsky proposed the S-80 design to the Marines in 1968. The Marines considered this a good, quick solution, and funded development of a testbed helicopter. Changes on the CH-53E also included a stronger transmission and a fuselage stretched 6 feet 2 inches (1.88 m). The main rotor blades' material was changed to a titanium-fiberglass composite. A new automatic flight control system was added. The vertical tail was also enlarged, with the tail rotor tilted upwards slightly to provide some lift in hover.
The initial YCH-53E first flew in 1974. Following successful testing, the initial production contract was awarded in 1978, and service introduction followed in February 1981. The US Navy acquired the CH-53E in small numbers for shipboard resupply. The Marines and Navy acquired a total of 177. For the airborne mine countermeasures role, the Navy later ordered a CH-53E version designated "MH-53E Sea Dragon" with enlarged sponsons and fuel tanks for greater fuel storage. The Navy began using the MH-53E in 1986. The Navy obtained 46 Sea Dragons.
CH-53K
The USMC had planned to upgrade most CH-53Es to keep them in service, but this plan stalled. Sikorsky proposed a new version, originally designated "CH-53X"; in April 2006, the USMC signed a contract for 156 aircraft as the "CH-53K" valued at $18.8 billion with deliveries to be completed by 2021. The USMC planned to start retiring CH-53Es in 2009, thus needing replacements quickly as some rotorcraft reached their structural life limits in 2011–12. Flight testing of the CH-53K was expected to begin in 2011.
The CH-53K is a general redesign of the CH-53E. The main improvements are new engines and cockpit layout. The CH-53K will have over twice the lift capacity and radius of action of the CH-53E, and a wider cargo hold to allow it to carry a Humvee internally. The CH-53K will feature new stubby composite sponsons to cut overall width, resulting in a narrower footprint for shipboard operations. It will also be equipped with a new composite rotor blade system, with technology similar to that found on the UH-60 Black Hawk helicopter. The CH-53K will use the General Electric GE38-1B engine, selected over the Pratt and Whitney Canada PW150 and a variant of the Rolls-Royce AE 1107C-Liberty used on the V-22 Osprey.
In August 2007, the USMC increased its order of CH-53Ks from 156 to 227. In 2007, first flight was planned for November 2011 with initial operating capability (IOC) by 2015. When the CH-53K enters service, it will serve as the USMC's heavy lift helicopter with the MV-22 (medium lift) and UH-1Y (light lift). RAND released a report in 2007 on seabasing that suggested a higher ratio of CH-53Ks to MV-22s would reduce deployment times from naval ships.
In 2008, design work was well underway, while weight reduction efforts to meet operational requirements were progressing. Increases in engine performance and rotor blade improvements are options to help meet requirements if needed. The rotor mast tilt was decreased and components shifted to ensure the center of gravity does not shift too far rearward as fuel is burned. The design requirements were 'frozen' in 2009–10 and not changed since.
On 22 January 2010, Sikorsky opened a $20 million Precision Components Technology Center in Stratford, Connecticut, which shall produce CH-53K elements, such as the rotating and stationary swashplates, main and tail rotor hubs, and main rotor sleeves. On 3 August 2010, the CH-53K passed its Critical Design Review (CDR), becoming ready for test production. However, the IOC fielding date was deferred to 2018. Sikorsky proposed building four pre-production aircraft for evaluation.
On 4 December 2012, Sikorsky delivered the first CH-53K, a Ground Test Vehicle (GTV) airframe. Preliminary tests included calibrating the aircraft's fuel system and attaching measuring devices at various test locations on the airframe to record temperature, aerodynamic loads, pressure, and vibrations. Two additional static ground test articles underwent structural testing at the firm's main manufacturing plant in Stratford, Connecticut.
In January 2013, the program was estimated to cost US$23.17 billion after procurement of the planned 200 CH-53Ks. In April 2013, the U.S. Navy program manager stated that development was "proceeding so well" that it might become operational ahead of schedule. Flight testing was planned for 2015, being delayed by over a year by faulty components.
On 31 May 2013, the Navy awarded Sikorsky a $435 million contract to deliver four prototype CH-53Ks for operational evaluation and mission testing; Sikorsky says the first two prototypes will examine structural flight loads while the third and fourth vehicles will focus on validating general performance, propulsion and avionics.
On 1 October 2013, Sikorsky issued an $8.5 million contract to Kratos Defense & Security Solutions for the design and development of maintenance training systems for the CH-53K, including a full-fidelity Maintenance Training Device Suite (MTDS) and a Helicopter Emulation Maintenance Trainer (HEMT). The MTDS provides a realistic environment for training and evaluating maintainers of the CH-53K's various subsystems, such as avionics, electrical, and hydraulic systems. The HEMT uses a 3D virtual environment to support maintenance training scenarios, including functional tests, fault isolation, troubleshooting, and remove and installation for 27 subsystems.
On 24 January 2014, the CH-53K GTV ignited its engines, spinning the rotor head without rotors attached. Low-rate production is planned to proceed from 2015 to 2017. Initial operating capability (IOC) was set to occur in 2019, with full-rate production commencing between then and 2022. The USMC intends to have eight active CH-53K squadrons, one training squadron, and one reserve squadron. In April 2014, testing with blades attached began, system integration followed. Flight testing was set to start in late 2014, each test aircraft flying approximately 500 hours over three years. The maiden flight was delayed, due to issues with the titanium quill shafts in the transmission and gear box.
On 5 May 2014, General James F. Amos announced during the CH-53K's official rollout that it will be called the "King Stallion". On 27 October 2015, the CH-53K took its first flight. On 7 March 2018, one lifted a payload of 36,000 pounds (16,330 kg), the maximum weight on the single center point cargo hook. The first CH-53K was delivered to the USMC on 16 May 2018; at the time, 18 additional helicopters were in production, and the second was planned for delivery in early 2019.
In December 2018, the CH-53K was projected to not be ready for combat as expected in late 2019, due to delivery delays caused by technical flaws found in testing, which resulted in a major program restructuring. Flaws included the engine re-ingesting exhaust gas, limited service life for the rotor gear boxes, late deliveries of redesigned parts, and deficiencies with the tail rotor and driveshaft. It is estimated that the delay will push back delivery of combat-ready CH-53Ks until May 2020.
The US Marine Corps received its first CH-53K simulator at Marine Corps Air Station New River in Jacksonville, North Carolina on 1 May 2020. It is a Containerized Flight Training Device (CFTD) built by Lockheed Martin, Sikorsky's parent company.
Design
The CH-53K is a general redesign with new engines and cockpit layout.[9] The CH-53K will use General Electric T408 (GE38-1B) engines rated at 7,500 shp (5,600 kW) each and will be able to fly 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph) faster than its CH-53E predecessor.
It will feature a new digital glass cockpit with fly-by-wire controls and haptic feedback, HUMS, a new elastomeric hub system, and composite rotor blades to improve "hot and high" performance. The split torque gearbox with quill shafts started development around 2007. The gearbox assembly including rotor hub and rotating control system weighs around 11,650 lb (5,280 kg), which is heavier than an empty Black Hawk helicopter. The split torque gearbox weighs 5,270 lb (2,390 kg). By comparison, the twin-engine Mil Mi-26 split torque gearbox weighs 8,020 lb (3,639 kg).
The CH-53K will also include an improved external cargo handling system, survivability enhancements, and improvements to extend service life. The cabin will be 30 ft (9.14 m) long by 9 ft (2.74 m) wide by 6.5 ft (1.98 m) tall. Its cabin will be 1 ft (30 cm) wider and 15% larger, but will have new shorter composite sponsons.
The CH-53K is to surpass the capability of the CH-53E by carrying nearly double the external payload of 27,000 lb (12,200 kg) over the same radius of 110 nmi (204 km). The CH-53K's payload reaches a maximum of 35,000 lb (15,900 kg). The CH-53K's maximum gross weight will be 88,000 lb (39,900 kg), which is increased over the CH-53E's 73,500 lb (33,300 kg). The CH-53K will keep approximately the same footprint as the CH-53E.
The CH-53K can carry two 463L master pallets, eliminating the need to break apart pallets between airlifter and helicopter.
Major subcontractors include Aurora Flight Sciences (main rotor pylon), Exelis Aerostructures (tail rotor pylon and sponsons), GKN Aerospace (aft transition), Onboard Systems International (external cargo hook system), Rockwell Collins (avionics management system), Sanmina-SCI Corporation (Intercommunications System), and Spirit AeroSystems (cockpit and cabin).
Operational history
Germany
In February 2018, Sikorsky signed an agreement valued at around 4 billion euro with Rheinmetall to team up for the German Air Force's CH-53G heavy lift helicopter replacement program, in which the CH-53K is competing against the CH-47F Chinook offered by Boeing. The German Federal Ministry of Defence was expected to issue an official request for information in the second half of 2018, with a timeline to award a contract in 2020 and deliveries to begin in 2023 for an expected order of around 40 helicopters.
On 29 September 2020, the German Ministry of Defense cancelled the "Schwerer Transporthubschrauber" (STH) heavy-lifting helicopter program for 45 to 60 helicopters after being judged too expensive and stated that its CH-53Gs are to be replaced "in a timely manner" after the project is "reexamined".
Israel
In 2009, the Israeli Air Force (IAF) said it would evaluate the new variant after it flies. In August 2015, it formalized a requirement for the CH-53K, listing the type as a "very high priority" item to enable the service to perform missions only the platform is capable of. Israel's current CH-53 "Yasur" fleet is to remain operational until 2025.
The CH-53K is competing with the Boeing CH-47F Chinook for an order of approximately 20 helicopters to replace the IAF's current CH-53 Yasur fleet.
Japan
- Japan has reportedly shown interest in the CH-53K.
Operators:
- United States
- United States Marine Corps.
Specifications (CH-53K)
General characteristics:
- Crew: 4
- Capacity: 30 passengers or troops / 24x casualty litters 35,000 lb (15,876 kg) payload
- Centre external load hook rating - 36,000 lb (16,329 kg)
- Fore and aft external load hooks rating - 25,200 lb (11,431 kg)
- Internal cargo system:
- Floor loading 300 lb/sq ft (1,464.73 kg/m2)
- Standard 6x 2,500 lb (1,134 kg) USMC 40 in × 48 in (1,016 mm × 1,219 mm) wooden pallets
- Full 463L Pallets 2x 10,000 lb (4,536 kg)
- Half 463L Pallets 5x 5,000 lb (2,268 kg)
- Tactical Bulk Fuel Delivery System 3 x 800 US gal (666 imp gal; 3,028 l) tanks
- Length: 99 ft (30 m) rotor and tail un-folded
- 73 ft 1.5 in (22.29 m) fuselage
- 83 ft 9 in (25.53 m) fuselage with refuel probe retracted
- 94 ft 11.5 in (28.94 m) fuselage with refuel probe extended
- Width: 17 ft 6 in (5.33 m) fuselage
- Height: 28 ft 4.9 in (8.659 m) rotor and tail un-folded
- Cabin Length: 30 ft (9.1 m)
- Cabin Width: 8 ft 7.2 in (2.6 m)
- Cabin Height: 6 ft 6 in (2.0 m)
- Max takeoff weight: 88,000 lb (39,916 kg) with external load
- 74,000 lb (33,566 kg) with maximum internal load.
Fuel capacity:
- 2,286 US gal (1,903 imp gal; 8,650 l) internal in two cells per sponson (15,545 lb (7,051 kg))
- 2,400 US gal (2,000 imp gal; 9,100 l) auxiliary internal in three cabin tanks (16,320 lb (7,403 kg))
- Powerplant: 3 × General Electric T408 (GE38-1B) turboshaft engines, 7,500 shp (5,600 kW) each.
Performance:
- Cruise speed: 170 kn (200 mph, 310 km/h)
- Range: 460 nmi (530 mi, 850 km)
- Combat range: 110 nmi (130 mi, 200 km)
- Service ceiling: 16,000 ft (4,900 m) ISA
- 13,200 ft (4,023 m) ISA +24 °C (75 °F).
(Web, Google, Jane’s, Wikipedia, You Tube)